Graphical Abstract
Abstract
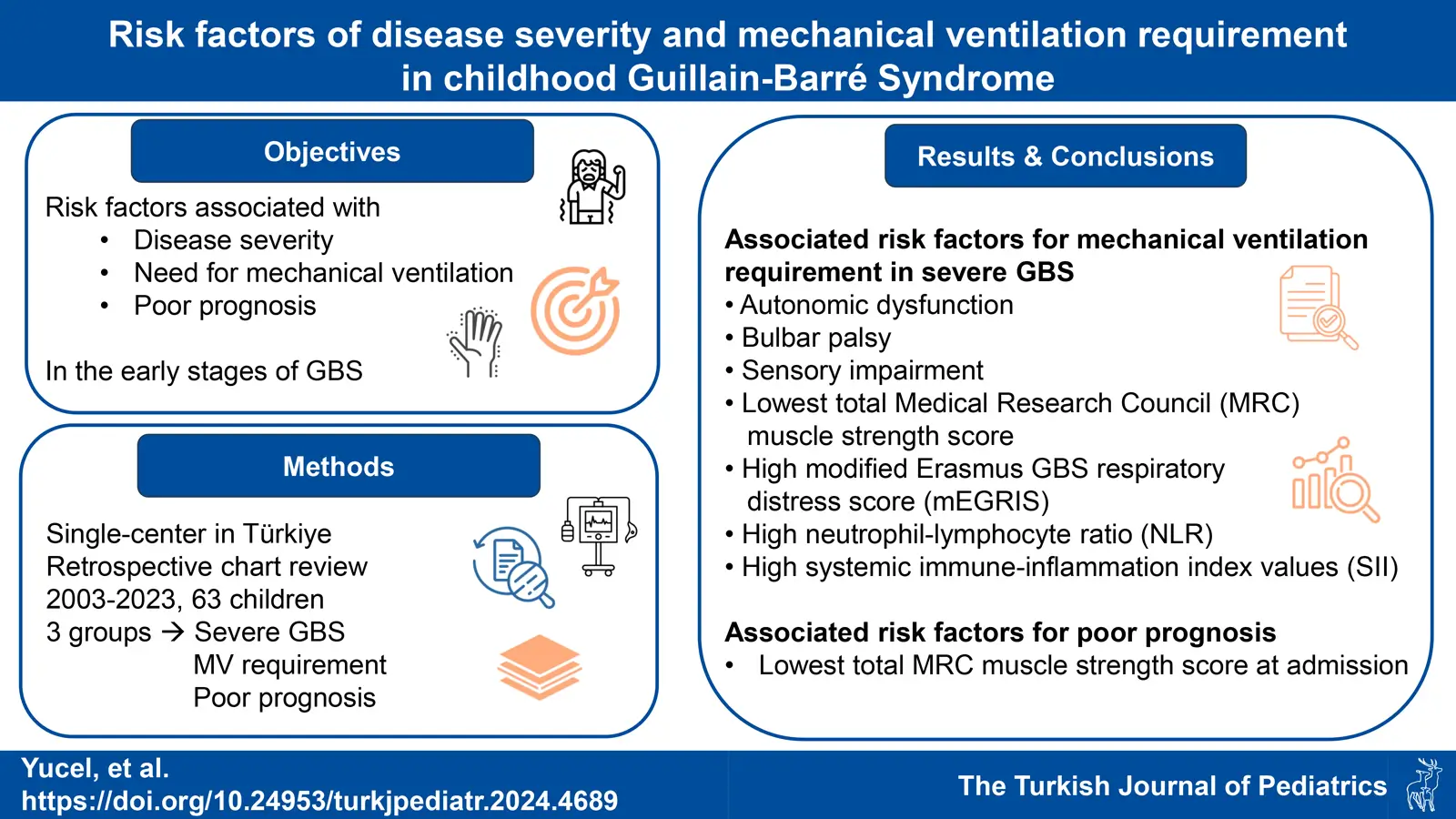
Background. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors associated with the severity of the disease, the need for mechanical ventilation (MV) and poor prognosis in the early stages of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS).
Methods. Data of children who met GBS diagnostic criteria were evaluated retrospectively. The sample was divided into three binary subgroups according to severe GBS (Hughes Functional Grading Scale [HFGS] ≥ 4 at admission), mechanical ventilation (MV) requirement, and poor prognosis (inability to walk independently, HFGS ≥ 3 after six months). Various clinical, laboratory and electrophysiological parameters were compared between these subgroups.
Results. The mean age of 63 children with GBS was 91.55±49.09 months. 13 (20.6%) patients required MV and 4 (6.3%) patients died. Associated risk factors for the need for MV in severe GBS were found to be autonomic dysfunction, bulbar palsy, sensory impairment, lowest total Medical Research Council (MRC) scale for muscle strength score at admission, high modified Erasmus GBS respiratory failure score (mEGRIS), high neutrophil-lymphocyte ratios (NLR) and high systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) values (p<0.001, p=0.003, p=0.033, p<0.001, p<0.001, p=0.037 and p=0.042, respectively). The lowest total MRC scale for muscle strength score at admission was a significant indicator of poor prognosis (p<0.001).
Conclusions. Autonomic dysfunction, bulbar palsy, sensory impairment, lowest total MRC scale for muscle strength score at admission, high mEGRIS score, high NLR and SII values are potential risk factors for the need for MV in children with severe GBS. The lowest total MRC scale for muscle strength score at admission was associated with poor prognosis.
Keywords: Guillain-Barré Syndrome, disease severity, mechanical ventilation, prognosis, risk factors, pediatric
References
- Sejvar JJ, Baughman AL, Wise M, Morgan OW. Population incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2011; 36: 123-133. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324710
- Willison HJ, Jacobs BC, van Doorn PA. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet 2016; 388: 717-727. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00339-1
- van Doorn PA, Van den Bergh PYK, Hadden RDM, et al. European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on diagnosis and treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2023; 28: 535-563. https://doi.org/10.1111/jns.12594
- Walgaard C, Lingsma HF, Ruts L, et al. Prediction of respiratory insufficiency in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol 2010; 67: 781-787. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21976
- Orlikowski D, Porcher R, Sivadon-Tardy V, et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome following primary cytomegalovirus infection: a prospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 52: 837-844. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir074
- Sharshar T, Chevret S, Bourdain F, Raphaël JC; French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Early predictors of mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Crit Care Med 2003; 31: 278-283. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200301000-00044
- Islam Z, Jacobs BC, van Belkum A, et al. Axonal variant of Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with Campylobacter infection in Bangladesh. Neurology 2010; 74: 581-587. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181cff735
- Kannan Kanikannan MA, Durga P, Venigalla NK, Kandadai RM, Jabeen SA, Borgohain R. Simple bedside predictors of mechanical ventilation in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Crit Care 2014; 29: 219-223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.10.026
- Tan CY, Razali SNO, Goh KJ, Shahrizaila N. The utility of Guillain-Barré syndrome prognostic models in Malaysian patients. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2019; 24: 168-173. https://doi.org/10.1111/jns.12320
- Barzegar M, Toopchizadeh V, Maher MHK, Sadeghi P, Jahanjoo F, Pishgahi A. Predictive factors for achieving independent walking in children with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Pediatr Res 2017; 82: 333-339. https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2017.67
- Witsch J, Galldiks N, Bender A, et al. Long-term outcome in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome requiring mechanical ventilation. J Neurol 2013; 260: 1367-1374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6806-x
- Ning P, Yang B, Yang X, et al. A nomogram to predict mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barré syndrome patients. Acta Neurol Scand 2020; 142: 466-474. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.13294
- Durand MC, Porcher R, Orlikowski D, et al. Clinical and electrophysiological predictors of respiratory failure in Guillain-Barré syndrome: a prospective study. Lancet Neurol 2006; 5: 1021-1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70603-2
- Fokkink WR, Walgaard C, Kuitwaard K, Tio-Gillen AP, van Doorn PA, Jacobs BC. Association of Albumin Levels With Outcome in Intravenous Immunoglobulin-Treated Guillain-Barré Syndrome. JAMA Neurol 2017; 74: 189-196. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.4480
- Durand MC, Lofaso F, Lefaucheur JP, et al. Electrophysiology to predict mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur J Neurol 2003; 10: 39-44. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00505.x
- Luijten LWG, Doets AY, Arends S, et al. Modified Erasmus GBS Respiratory Insufficiency Score: a simplified clinical tool to predict the risk of mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2023; 94: 300-308. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2022-329937
- Hu MH, Chen CM, Lin KL, et al. Risk factors of respiratory failure in children with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Pediatr Neonatol 2012; 53: 295-299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedneo.2012.07.003
- Luo H, Hong S, Li M, Wang L, Jiang L. Risk factors for mechanical ventilation in children with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2020; 62: 214-218. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.26905
- Tiwari I, Alam A, Kanta C, et al. Clinical profile and predictors of mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barre syndrome in North Indian children. J Child Neurol 2021; 36: 453-460. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073820978020
- Roodbol J, Korinthenberg R, Venema E, et al. Predicting respiratory failure and outcome in pediatric Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2023; 44: 18-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2023.02.007
- Qinrong H, Yuxia C, Ling L, et al. Reliability and validity of prognostic indicators for Guillain-Barré syndrome in children. Dev Med Child Neurol 2023; 65: 563-570. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.15418
- Korinthenberg R, Schessl J, Kirschner J. Clinical presentation and course of childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome: a prospective multicentre study. Neuropediatrics 2007; 38: 10-17. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-981686
- Wu X, Li C, Zhang B, et al. Predictors for mechanical ventilation and short-term prognosis in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Crit Care 2015; 19: 310. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-015-1037-z
- Green C, Baker T, Subramaniam A. Predictors of respiratory failure in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med J Aust 2018; 208: 181-188. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja17.00552
- Hughes RA, Newsom-Davis JM, Perkin GD, Pierce JM. Controlled trial prednisolone in acute polyneuropathy. Lancet 1978; 2: 750-753. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92644-2
- Reisin RC, Pociecha J, Rodriguez E, Massaro ME, Arroyo HA, Fejerman N. Severe Guillain-Barré syndrome in childhood treated with human immune globulin. Pediatr Neurol 1996; 14: 308-312. https://doi.org/10.1016/0887-8994(96)00050-1
- Wen P, Wang L, Liu H, et al. Risk factors for the severity of Guillain-Barré syndrome and predictors of short-term prognosis of severe Guillain-Barré syndrome. Sci Rep 2021; 11: 11578. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91132-3
- Kleyweg RP, van der Meché FG, Schmitz PI. Interobserver agreement in the assessment of muscle strength and functional abilities in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1991; 14: 1103-1109. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.880141111
- Sarnaik AP, Clark JA, Sarnaik AA. Respiratory distress and failure. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme III JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2016: 528-536.
- Lawn ND, Fletcher DD, Henderson RD, Wolter TD, Wijdicks EF. Anticipating mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Neurol 2001; 58: 893-898. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.58.6.893
- Wang Y, Shang P, Xin M, Bai J, Zhou C, Zhang HL. The usefulness of chief complaints to predict severity, ventilator dependence, treatment option, and short-term outcome of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome: a retrospective study. BMC Neurol 2017; 17: 200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-017-0982-3
- Islam Z, Papri N, Ara G, et al. Risk factors for respiratory failure in Guillain-Barré syndrome in Bangladesh: a prospective study. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2019; 6: 324-332. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.706
- Henderson RD, Lawn ND, Fletcher DD, McClelland RL, Wijdicks EF. The morbidity of Guillain-Barré syndrome admitted to the intensive care unit. Neurology 2003; 60: 17-21. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000035640.84053.5b
- Orlikowski D, Sharshar T, Porcher R, Annane D, Raphael JC, Clair B. Prognosis and risk factors of early onset pneumonia in ventilated patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Intensive Care Med 2006; 32: 1962-1969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-006-0332-1
- Zahorec R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, past, present and future perspectives. Bratisl Lek Listy 2021; 122: 474-488. https://doi.org/10.4149/BLL_2021_078
- Sarejloo S, Khanzadeh S, Hosseini S, et al. Role of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in Guillain Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mediators Inflamm 2022; 2022: 3390831. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3390831
- Wu X, Wang H, Xie G, Lin S, Ji C. Increased systemic immune-inflammation index can predict respiratory failure in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurol Sci 2022; 43: 1223-1231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05420-x
- van den Berg B, Bunschoten C, van Doorn PA, Jacobs BC. Mortality in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Neurology 2013; 80: 1650-1654. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182904fcc
- Rangan RS, Tullu MS, Deshmukh CT, Mondkar SA, Agrawal M. Clinical profile and outcome of Guillain-Barre syndrome in pediatric patients admitted to a tertiary care centre: a retrospective study. Neurol India 2021; 69: 81-84. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.310112
- Shibeshi MS, Mengesha AA, Gari KT. Pediatric Guillain-Barré syndrome in a resource limited setting: clinical features, diagnostic and management challenges, and hospital outcome. Pediatric Health Med Ther 2023; 14: 107-115. https://doi.org/10.2147/PHMT.S401461
- Konuşkan B, Okuyaz Ç, Taşdelen B, Kurul SH, Anlar B; Turkish Childhood Guillan-Barre Syndrome Study Group. Electrophysiological subtypes and prognostic factors of childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome. Noro Psikiyatr Ars 2018; 55: 199-204. https://doi.org/10.5152/npa.2017.16996
Copyright and license
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited.















